Mealtime And Children With Autism: Dealing With Picky Eaters
Some children or even adults have certain preference towards food. Does that make them picky eaters?
What is the difference between children having preference in food and a picky eater?
Food preference includes eating different types of food which are usually influenced by cultures and exposure in one's life. However, a child who is a picky eater limits himself to eat fewer types of food. They refuse many food types and are very reluctant to try new food.
About 75% of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) have picky eating issues, which is much higher compared to the 25-35% of typically developed toddlers (Martins, Young, & Robson, 2008), this is very concerning as it may affect a child's growth and development. Thus, we must recognise signs of picky eating as early as possible.
There are several signs your child may exhibit as a picky eater
Here's what to look out for:
- They tend to eat food from the same group (same texture, taste, and smell) and exclude other food groups majority of the time
- They dislike to try new food with different flavours, textures, smell, or even different shape, and may show tantrums or melt down when given new food
- They may eat a lot of snacks and eat less during mealtime
- They may prefer foods that are sweet or bland or with specific textures
It is also important for us to understand the reason behind why the child is a picky eater for us to address and help the child. The following are some of the common reasons:
1. Gastrointestinal problems
First and foremost, parents need to rule out health related issues that may lead to a child being a picky eater, such as gastrointestinal problems (bloating, acid reflux, or constipation).
A study found that some children, who have picky eating habits, have gastrointestinal problems (Yang, et al., 2017). When eating certain food, the child may feel discomfort thus they tend to be very cautious about what they eat.
As many ASD children have problems communicating verbally; informing parents that they are uncomfortable or in pain may not be something they are able to do. Therefore, parents need to be alert and identify if their picky eating or cranky behaviours during mealtime are due to more serious issues.
2. Restricted interest and repetitive behaviour
Children with ASD tend to have restricted interests and repetitive behaviours, which contribute to their inability to eat a variety of food.
Their tendency to prefer sameness and inflexibility may lead them to become picky eaters as they would insist on food of the same colour, same type of food, same brand, or even eating from the same restaurant (Baraskewich, von Ranson, McCrimmon, & McMorris, 2021).
3. Sensory related issues
The majority of children with ASD have sensory related problems, this can include picky eating.
They may be overly sensitive towards certain tastes, smells, textures, or visual presentations of the food, which affects their ability to accept and eat a variety of food.
What impact does picky eating have on a child?
Sleep disturbance
Some picky eaters face sleep disturbance. This may be due to the type of food they take or even due to gastrointestinal issues. Sleep disturbance will eventually lead to challenging behaviours, poor attention, and reduced ability to learn new skills (Yang, et al., 2017).
Undernutrition
It is a concern that some picky eaters may lack nutrition as their preferred diet does not fulfill the required nutrition, which may impact their growth and development.
Higher risk of being overweight or obese
On the other hand, some may have higher risks of being overweight or obese due to their unhealthy preferred diet, for example food with high sugar content (sweets, chocolate), junk food, or fast food.
Increased stress in the family
Parents and siblings may have to compromise around mealtime routines to accommodate the picky eater child. Family members may feel stressed as they must constantly follow the child's food preference and need to eat the same meal all the time.
Stress also increases as family has to face behaviour issues during mealtimes such as meltdowns, spitting food, or unwillingness to sit at the family table. Mealtime does not become a positive activity, instead it's a stressful event.
Reduced opportunity to socialise
Picky eating may lead to reduced opportunity for the child to participate in social activities with family and peers. They may not be able enjoy having meals together at family events or the school canteen as their preferred food may not be available. This ultimately reduces the opportunity for family mealtime or eating out.
Strategies that can help picky eaters:
1. Rule out medical related problems.
2. Be patient and take it slow. Your child may struggle and refuse to cooperate. Keep calm, and try to make mealtime fun and enjoyable. It will take time before a child can overcome this issue.
3. Allow your child to play with food. Begin introducing food through play instead of directly feeding. For example, allow your child to use their hands to feel and smell the food before asking them to taste it.
4. Focus on one food at a time. For example, introduce noodles with different shapes and colours over a period of time, along with their usual food. Don't add on fruits and vegetables at the same time as this can be overwhelming.
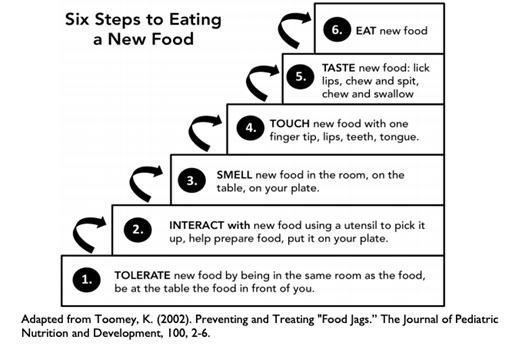
5. Use the graduated exposure method (Kay Toomey's Sequential Approach). If your child loves to eat a certain type of food, introduce them to similar food with a slight change. For example, if your child loves chicken nuggets, introduce them to chicken nuggets with different textures or try small breaded chicken breast. Avoid introducing food with tastes and smells that are very different from their preferred food such as shrimp or fish.
6. Record progress. Every small change is a success. Appreciate every effort your child portrays. For example, even if your child is only able to hold and put a new food near their mouth, this is considered an achievement.
7. Be consistent and do not give up. There is no quick fix in helping a picky eater.
These are only some of the strategies and tips to help children with picky eating issues. It is always the best idea to seek further advice from the professionals such as pediatricians, occupational therapists, dietitians, or nutritionists to understand and help the child overcome picky eating issues.
The National Autism Society of Malaysia (NASOM) is a national charitable organisation that strives to provide a range of support services for autistic people, especially children and their immediate family members
This article was contributed by Azmah Daud, Senior Occupational Therapist at NASOM Setia Alam. She has over 10 years experience working with autistic individuals.
If you'd like to contribute an article, email [email protected]