Do You Use Your Phone Before Sleeping? Here Are Reasons Why You Really Shouldn't
It affects your sleep way more than you think.
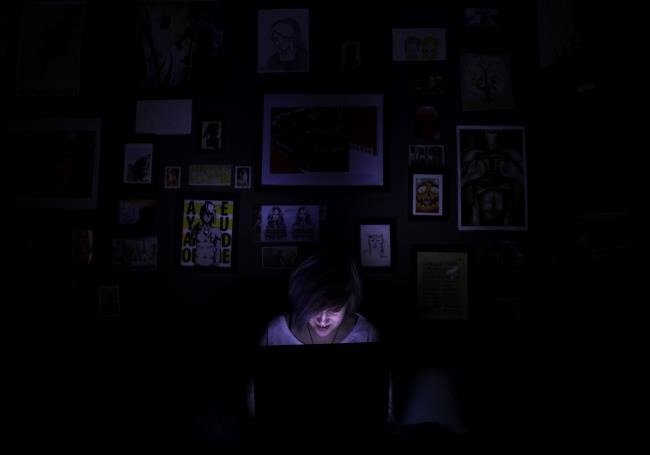
If you've been told time and again by your parents for using your phone (or any gadget in fact) in the dark, then - believe it or not - they are actually right to do so
Living as the generation of the internet and smartphone is difficult, especially for teenagers who want to stay in the loop with societies all over the world. When one is about to go to sleep in Malaysia, America would just be waking up. You may follow celebrities and microcelebrities on social media apps and follow their exciting lives on Instagram, Twitter or Youtube. Or, you may be messaging your friend or having a good old game of candy crush.
You think that you are 'winding down' and trying to fall asleep. But experts say that the light from the screen and mind activity is doing the exact opposite - that is keeping you awake.
Using your phone during the day is no problem, it's using it in the dark that's bad. And there's perfectly legit scientific explanation for this.
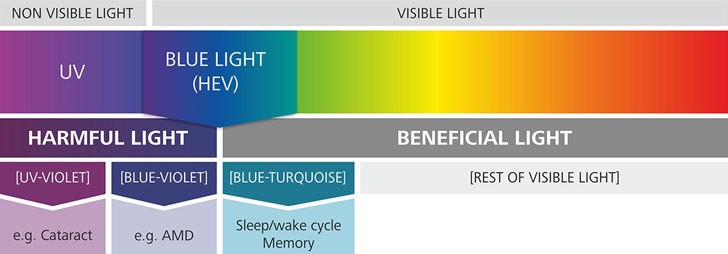
Your sleep-wake cycle, which is instrumental in alerting your body when it is time to be awake or going to sleep is determined by your circadian rhythm. The circadian system is a biological process where factors such as blood pressure, core body temperature and light determine your 24-hour processes.
The emission of blue light from your devices works the same way as any light source, such as the sun that gets your body ready for activity. Therefore, it doesn't make sense to be exposed to it before you settle down for the night. Clinical psychologist and sleep therapist, Dr. Michael J. Breus confirms that it keeps us from falling asleep.
“Blue runs in about the 460 nanometer range, in terms of the spectrum of light. That particular spectrum of light hits these cells and makes them send a signal to an area of the brain known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus and tells it to turn off melatonin production. Melatonin is the key that starts the engine for sleep.”
"We found that humans, like other organisms, are most sensitive to light stimuli during the biological night, and far less sensitive to light in the middle of the biological day," other studies show.
In the long run, not having enough sleep comes with a hefty side of negative health effects
You're probably already aware of the ton of health problems related to lack of sleep. No matter how tired you are of hearing them, they WILL affect you if you continue to have low quantity and quality of sleep.
Diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and according to the Harvard Medical School, potentially cancer due to low levels of melatonin are effects that may stem from a lack of quality sleep.
A Harvard study shed a little bit of light on the possible connection to diabetes and possibly obesity. The researchers put 10 people on a schedule that gradually shifted the timing of their circadian rhythms. Their blood sugar levels increased, throwing them into a prediabetic state, and levels of leptin, a hormone that leaves people feeling full after a meal, went down.
Stress is also a huge negative side effect, seeing as feeling sleepy equates to being grumpy and loss of focus. Having a terrible mood throughout the day not only throws you off your game at school or work, but dampens the environment for others around you. Don't be that party pooper.
You may find the quality of your work and your grades at school slowly starting to slip...
Even though you may be getting your full 8 hours of sleep, you may still feel tired when you wake up in the morning. Yes, blue light is anything with a light source, even the sun. But it intensifies if you use it in a dark surrounding and having it a few feet away from your face.
Results from a study specifically on the effects of using devices in bed with the lights out are not surprising. Xue Ming, professor of neuroscience and neurology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School with a study sample of 1,537 students across three high schools in New Jersey.
She found that students who turned off their devices or who messaged for less than 30 minutes after lights out performed significantly better in school than those who messaged for more than 30 minutes after lights out.
Students who texted longer in the dark also slept fewer hours and were sleepier during the day than those who stopped messaging when they went to bed.
However, not all hope is lost. For those who really can't put away their devices before bedtime...
We understand, it's just way too hard to stop something once it's a daily ritual. To lessen the power of the blue light, theres an app that automatically adjusts your device screen to the time of day by keying in your location.
For computer-in-bed users, this software that fights the blues at night by displaying warmer tones will come in handy.
There are also glasses that filters out blue light, causing less strain when you look at your devices for long time. Before you think that its absolutely crazy to buy a pair of glasses to look at your electronic devices think about this. Just like you would wear sunglasses to protect your eyes against strong UV rays from the sun, you would want to protect your eyes against blue rays from your devices that you prop it in front of your eyes.
Some may be skeptical about these, but it's worth the shot.